Cells, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-dependent signaling pathway is aberrantly activated in psoriatic lesions and contributes to disease pathogenesis. Among PI3Ks enzymes, PI3Kα, β, and δ isoforms are known to bind the p85 regulatory subunit and mediate activation of AKT and other downstream effectors. In this study, we deepened our understanding of the expression and function of PI3Kδ in skin lesions of patients affected by psoriasis. For the first time, we found that PI3Kδ is overexpressed in psoriatic plaques, and its expression is not only confined to infiltrating immune cells but also accumulates in proliferating keratinocytes of the epidermal basal layer. We investigated the function of PI3Kδ in psoriatic skin by evaluating the impact of seletalisib, a newly developed selective PI3Kδ inhibitor, in both in vitro and in vivo experimental models of psoriasis. Of note, we found that PI3Kδ sustains keratinocyte hyperproliferation and impaired terminal differentiation induced by IL-22, as well as induces epithelial inflammation and resistance to apoptosis mediated by TNF-α in human keratinocytes. Mechanistically, PI3Kδ promotes PDK1 phosphorylation and signals through AKT-dependent or -independent pathways. It is worth mentioning that PI3Kδ inhibition by seletalisib attenuates the severity of psoriasiform phenotype induced in the Imiquimod-induced mouse model of psoriasis by restoring the physiological proliferation and differentiation programs in epidermal keratinocytes and contrasting the cutaneous inflammatory responses. Therefore, we suggest PI3Kδ as a potential topically druggable target in psoriasis and skin diseases characterized by epidermal hyperproliferation and skin inflammation.
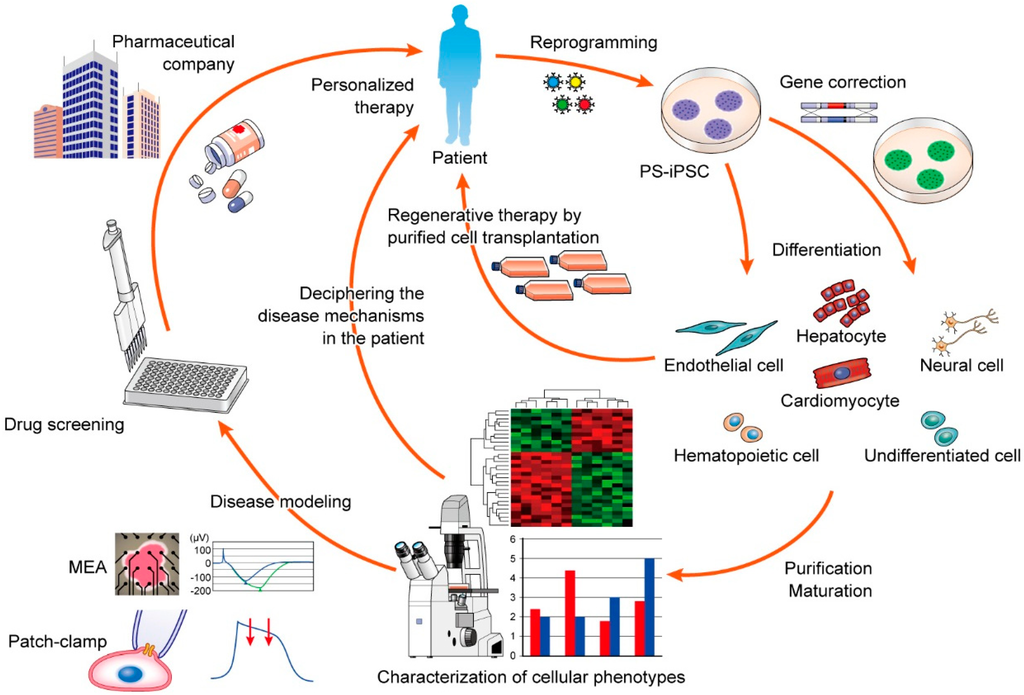
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Advancing synthetic biology through cell-free protein synthesis - ScienceDirect

Cell-free Macromolecular Synthesis
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology on X: From May cover Challenges and directions in studying cell–cell communication by #ExtracellularVesicles @DaveCarter1234 @guillaume_niel @VaderPieter Clayton Lambert & Raposo #EVsAreCool FREE pdf: https
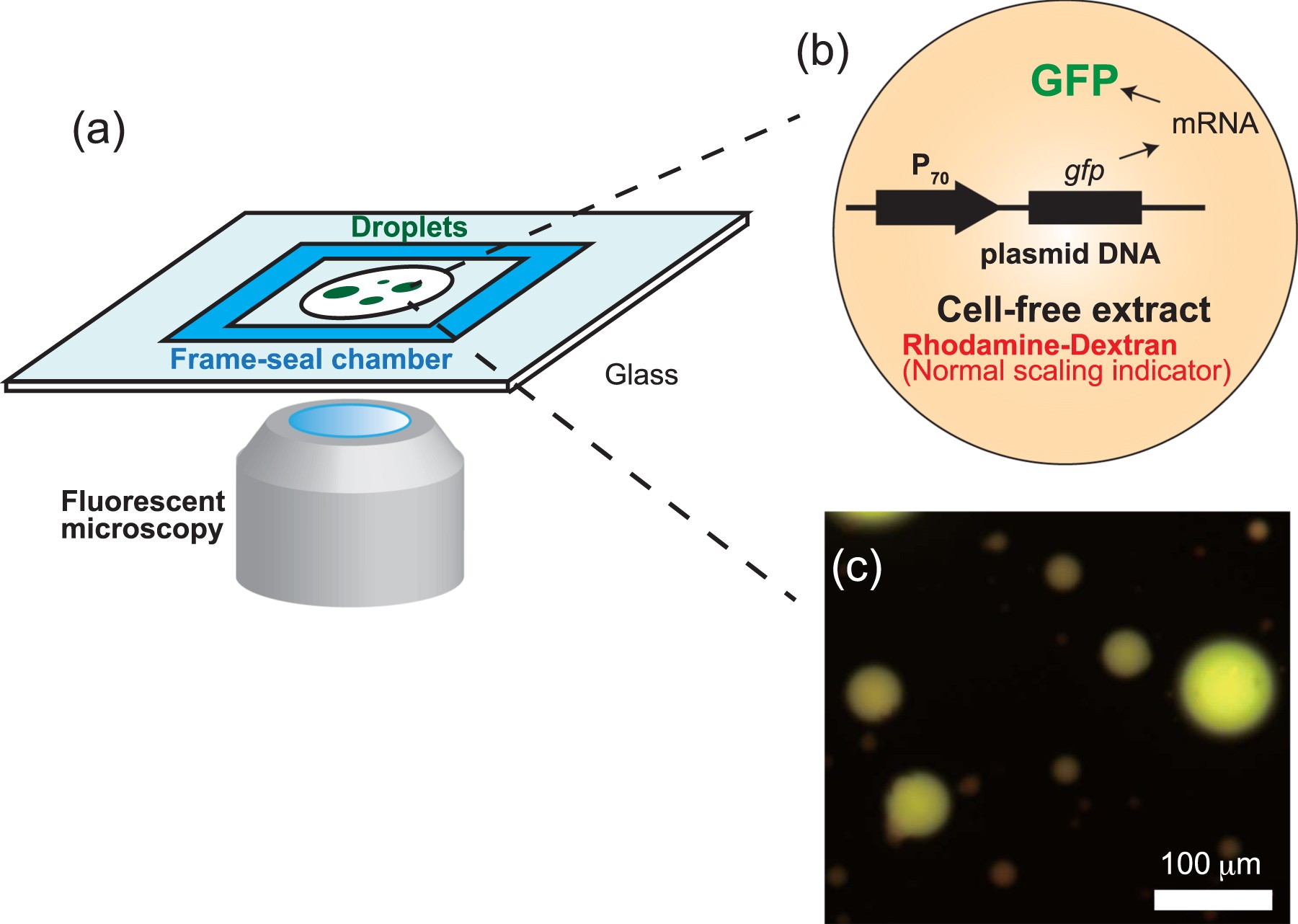
Anomalous Scaling of Gene Expression in Confined Cell-Free Reactions
Full-spectrum cell-free RAN for 6G systems: s
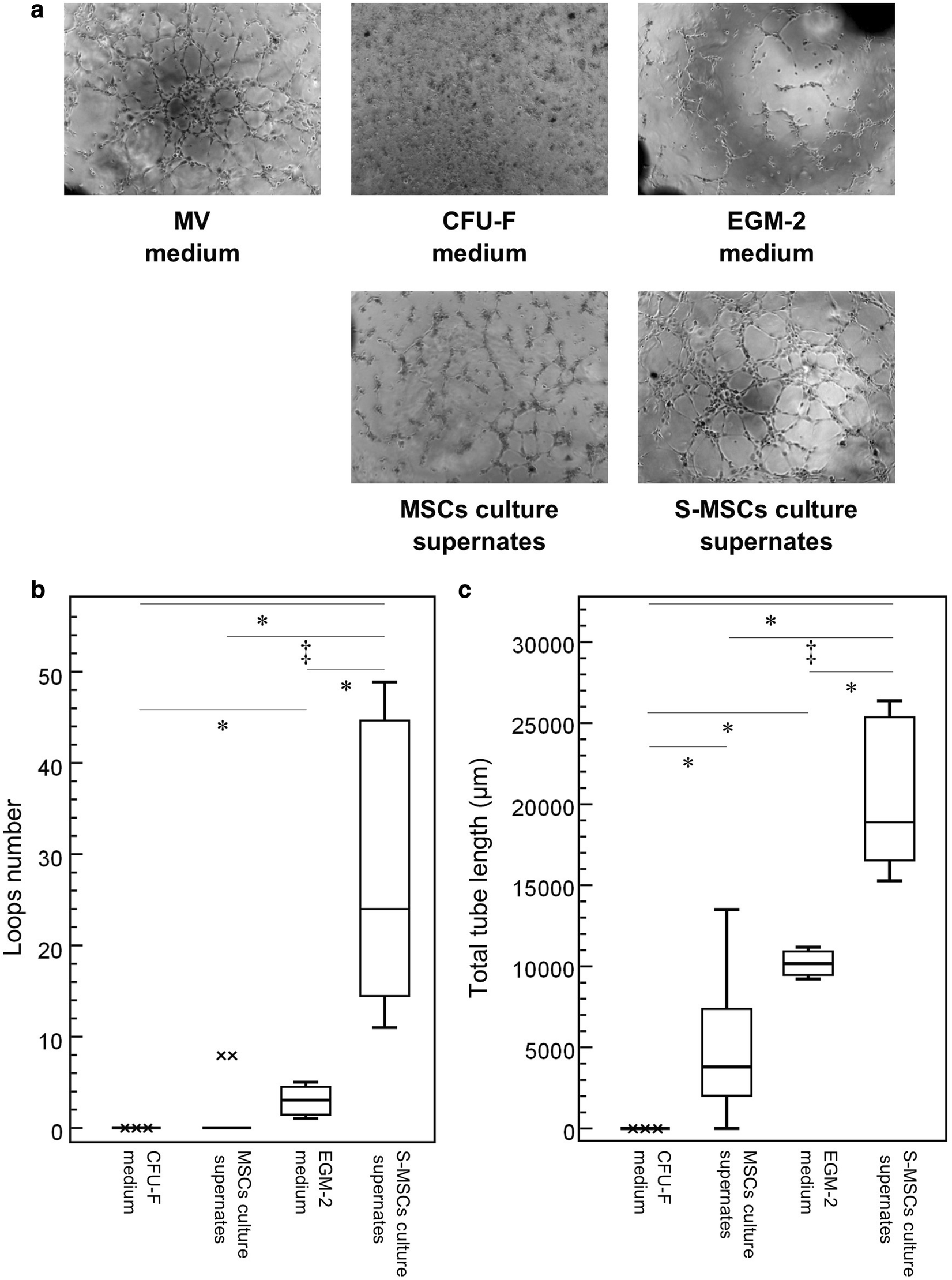
In vivo efficacy of endothelial growth medium stimulated mesenchymal stem cells derived from patients with critical limb ischemia, Journal of Translational Medicine
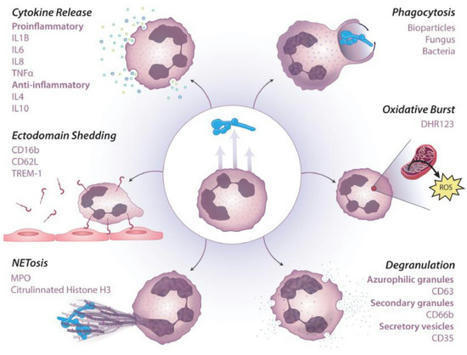
from Flow Cytometry to Cytomics, Page 2
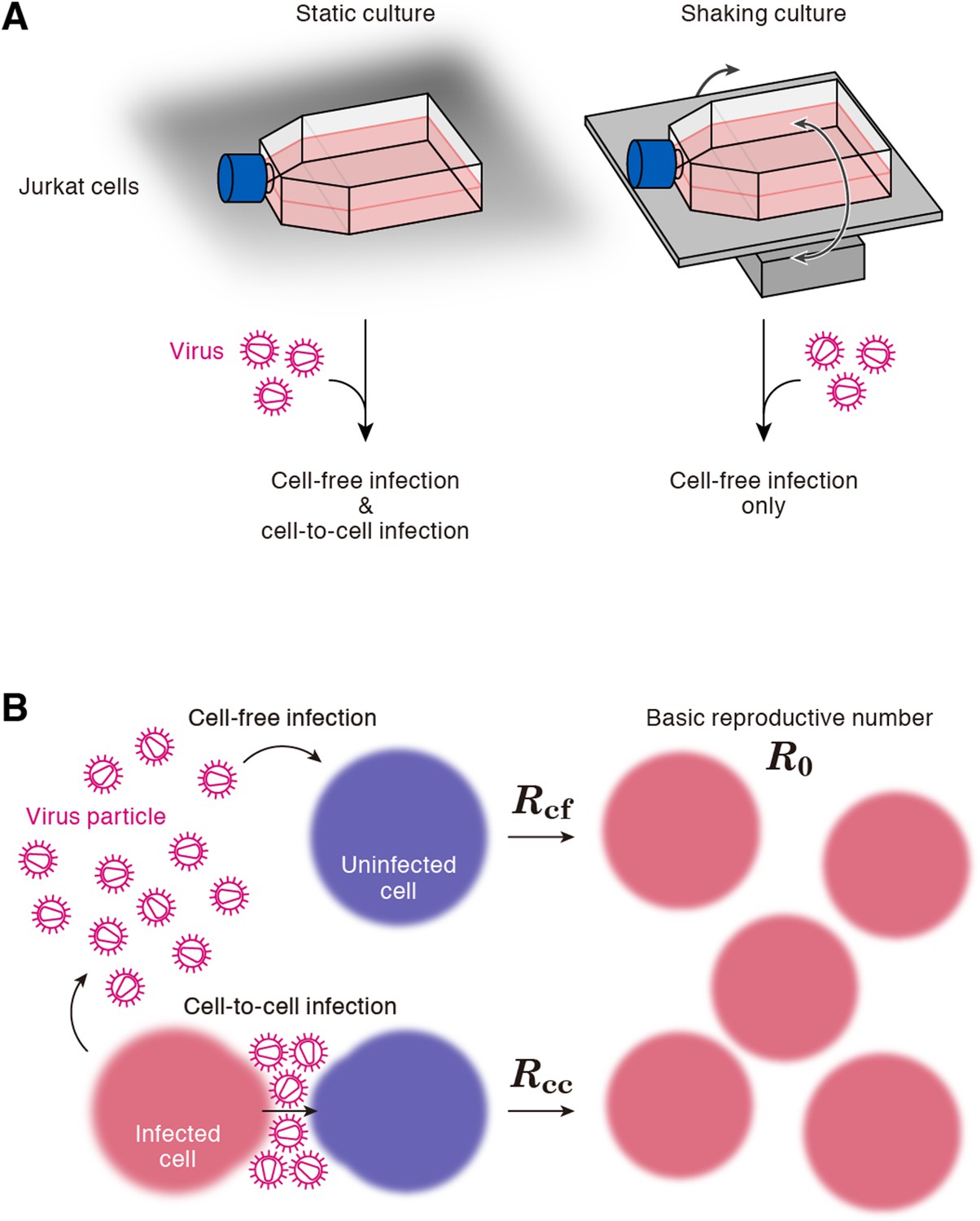
Cells, Free Full-Text
Cells, Free Full-Text
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)







